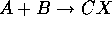 , can be factorized into three part:
, can be factorized into three part:


The cross section for the production of particle C in a collision
of hadron A
and hadron B, 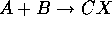 , can be factorized into three part:
, can be factorized into three part:
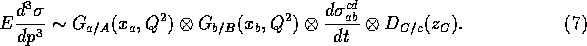
Similarly, the polarization dependent cross section can be described as
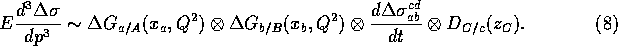
The polarization dependent cross section has been calculated in leading
order (LO) [11,12] and listed
in Table iii. If we choose the process
which is free from fragmentation such as high 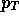 prompt photon
production, weak boson production (leptonic decay mode),
the experimentally measured asymmetry
can be directly connected to the products of two structure functions
prompt photon
production, weak boson production (leptonic decay mode),
the experimentally measured asymmetry
can be directly connected to the products of two structure functions
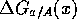 and
and 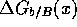 . In the case we know one of the
polarized structure functions, say
. In the case we know one of the
polarized structure functions, say 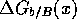 , we can
determine
, we can
determine 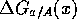 from the measurement.
from the measurement.
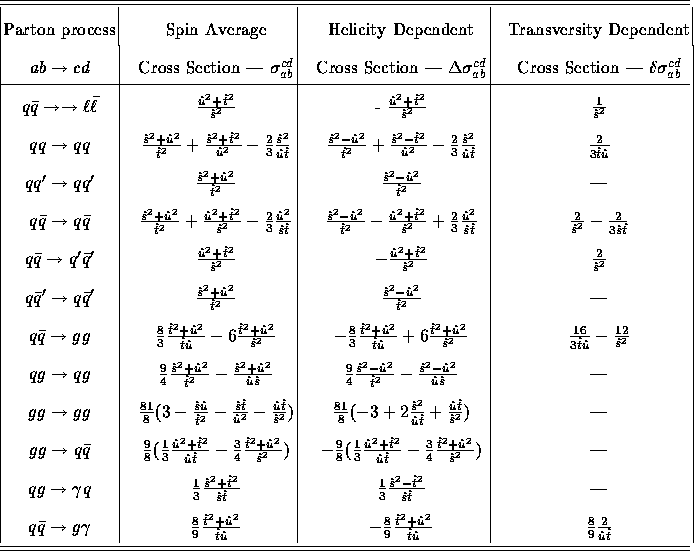
Table iii: Parton cross sections and asymmetries. Each entry multiplies a
factor of 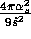 , except for the first (Drell-Yan)
which multiplies
, except for the first (Drell-Yan)
which multiplies 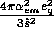 , and the last (prompt
, and the last (prompt
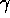 production) which multiplies
production) which multiplies
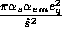 .
In addition, helicity entries multiply
.
In addition, helicity entries multiply 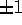 according to whether the
beam helicities are equal (+1) or opposite (-1), and
transversity entries
multiply the kinematic factor
according to whether the
beam helicities are equal (+1) or opposite (-1), and
transversity entries
multiply the kinematic factor 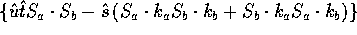 ,
which is proportional
to
,
which is proportional
to 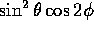 in the parton-parton center of mass frame.
in the parton-parton center of mass frame.
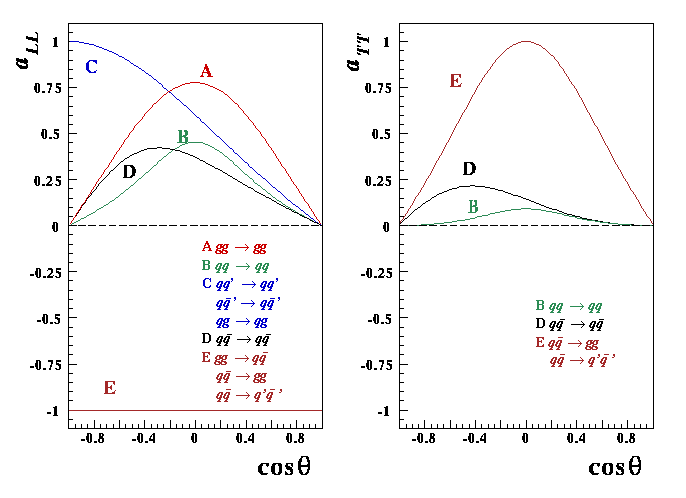
Figure 3: Asymmetries for the partonic processes,
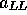 and
and 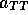 are plotted as functions of
the cosine of the scattering angle in the center-of-mass
system of interacting partons.
are plotted as functions of
the cosine of the scattering angle in the center-of-mass
system of interacting partons.